Troublesome Pests ...
American Cockroach — Periplaneta americana

This cockroach lives outdoors as well as indoors and often infests basements and sewer systems. These large cockroaches are
capable of flying, but usually remain on the ground. The female produces an egg case every month for about 10 months. There
are about 16 eggs per case.
Identification
Adults are about 1.5 inches long and shiny, light brown. There are yellow markings on the area behind the head. The immatures
are dark brown and black wings. The egg case is about 3/8 of an inch long and dark brown color.
Treatment
Limiting the movement of these cockroaches from sewer systems and basements may be done with screens placed over drains.
Sticky traps may help to locate infested areas. Chemical control in the form of sprays, dusts or baits directed at these
infested areas will provide control.
American Dog Tick — Dermacentor variabilis

The young and adult stages of this tick are external parasites of animals. The 3 immature stages require a blood meal from a different host in order to develop to the adult stage and to lay eggs.
Identification
This tick is about 1/8 inch long and is dark brown with an irregular pattern of white markings on the body area behind the head. It has 8 legs.
Treatment
Keep vegetation cut low to discourage small animal (rabbits, field mice) populations; use repellents on clothing when walking in areas infested with ticks. Liquid and granular insecticides applied in the spring may help with control.
Asian Ladybird Beetle — Harmonia axyridis

Adults and young stages are beneficial because they feed on aphids. The eggs are laid in the spring and the larvae and adults attack aphids. There are 2-3 generation per year. Adults gather in large numbers to over-winter. The adults may live 2-3 years and return to the same wintering site.
Identification
The ladybird beetles are about .25 inch long, and orange with black spots.
Treatment
Spray water on aggregations of the adults on the outside of the house in the fall. This may help to disperse them to another overwinter sites. Use the vacuum cleaner indoors to collect the adults.
Bed Bug — Bed Bug

Bed bugs feed on the blood of warm blooded animals, such as birds and bats. The bed bug that feeds on humans lives in the cracks and crevices of the bed or behind the baseboards and woodwork close to the bed.
Identification
These insects are about .25 inch long.Color ranges from dark red to almost black. They are primarily active at night, so the only evidence of their presence my be red bites that itch.
Treatment
Remove the mattress and vacuum it thoroughly. Clean all the cracks and crevices of the bed frame, and use some aerosol insecticides on the frame and adjacent baseboards and woodwork.
Black Widow Spider — Lactrodectus spp.

The black widow spider is found throughout the state. They feed on insects and other spiders that get trapped in their web. They are usually not aggressive , but if handled or accidentally touched they may bite. Their venom may cause pain and serious illness. If bitten you should place ice on the wound and seek medical attention.
Identification
The black widow spider has a somewhat round, shiny black abdomen with red markings on the underside. Outside they live under rocks and tree limbs. Around the house they are often found in wood piles. Inside they may be found in basements and crawlspaces, and in secluded places in buildings.
Treatment
Wear gloves when working around wood piles or moving items in sheds and garages. Be cautious of spider webs when working in basements and crawlspaces. Use aerosol insecticides to control the spiders.
Boxelder Bug — Boisea trivittata

The adults and young stages feed on the seeds and stems of boxelder and other maple trees. There is usually 1 generation per year, and the adults (and sometimes large nymphs) overwinter in masses in protected locations around the outside of structures. Sometimes adults will enter houses in small to large numbers. They do not bite but may stain fabric and carpet if crushed.
Identification
These bugs are about ½ inch long and are brownish black with red markings on the thorax and wings. The immature stages are colored red with reduced wings. Earwigs are commonly found on trees in the maple family, and are numerous where boxelder trees grow. Often they will gather in large numbers in the fall.
Treatment
Removing boxelder or other maple trees is not recommended, since these insects may find food at other locations and overwinter at houses without the trees nearby. Disrupting the masses of bugs in the fall, and spraying with insecticide will help to reduce overwintering populations.
Brown Recluse Spider — Loxoceles reclusa

This poisonous spider has been found in numerous places throughout the state, but only rarely have there been serious infestations. They may be active throughout the year, but often remain unnoticed because of their reclusive habits. They may bite if handled or trapped in shoes or clothing. The venom produces a severe sore that is slow to heal.
Identification
The spider is light brown, about .50 inch in length, and has a violin-shaped marking on the thorax. These spiders make an irregular and sticky web. Adults may be found in dark, secluded places inside; in Virginia they are not commonly found outdoors. They are most commonly found behind baseboards, under tables and chairs form the basement to the attic, and in garages and sheds.
Treatment
Wear gloves when working around boxes of old clothing or material that has been undisturbed for a long period. Use sticky traps in areas suspected of having an infestation. Use spray insecticides to control spiders in difficult to clean spaces.
Banded Cockroach — Supella longipalpa

The cockroach lives indoors in habitats similar to the German cockroach, but will also infest other rooms of the house besides the kitchen and bathroom. The female can produce about 14 egg cases during her life and each contains about 18 eggs.
Identification
The adults are about .5 inch long and brown with distinct bands on the abdomen. The dark brown wings are short in the female and cover the abdomen in the male. The young are yellowish-brown and lack wings. The egg case is about .25 inch long and light brown.
Treatment
Removing food scraps and water sources will help to limit these pests. Use sticky traps to locate infested sites. Chemical control in the form of sprays, dusts or baits directed at these sites may control severe infestations.
Carpenter Ant — Camponotus spp.

Nests are usually located in damp, damaged wood, but they can infest good wood. The workers forage for food inside in early spring, then move outside to feed on insects. Colonies located inside usually become active about February and March.
Identification
These ants are .25 to .5 inch long, and may be black or red. The antennae are long. Worker ants may be seen inside throughout the year. The large, winged queens appear in the spring.
Treatment
Locating the nest is the first step in controLling them. Inspect for water leaks and damaged wood, and remove the wood and repair any water leaks. Baits can be effective whereas spraying may not.
Carpenter Bee — Xylocopa micans

Carpenter bees resemble bumblebees but they are not social insects, and most of the top part of their abdomen is without hairs. The males lack a sting, and the females possess a potent sting but they rarely use it.
Identification
Carpenter bees are large and have a blue-black, green or purple metallic sheen. They often burrow into exposed dry wood of buildings. Infestations are often detected by finding sawdust on the ground below the area being drilled. The galleries are made by the female and usually average 5 inches in length. She then furnishes the nest with "bee bread" (a mixture of pollen and regurgitated nectar) and lays an egg on top of it. The female then closes the cell with chewed wood pulp. There may be a number such sealed cells in a linear row in one gallery.
Treatment
Treat infestations on a case by case basis. Damage to wood from the drilling activity of a pair of carpenter bees is slight, the activities of many bees during a period of years can cause considerable damage.
Carpet Beetle — Attagenus spp.

The larvae of carpet beetles feed on animal products including wool, leather, and fur. Other species feed on stored food. Adults usually live outside and feed on the pollen of plants. The larvae may require 2-3 months to complete development and during this time may shed their skin a few times.
Identification
The adult carpet beetle is about .10 inch long and has different color patterns.And the larvae are light brown with brown hairs extending from the sides and tail. Holes in carpets, blankets, and clothing are usually caused by the larvae feeding.
Treatment
Clothing and carpeting that can be damaged by carpet beetles should be cleaned regularly, and wool and leather clothing stored in sealed containers. Regular cleaning of closets and storage areas will help to reduce infestations.\r\n
Clothes Moth — Tineola sp., Tinea sp.

The caterpillar feeds on wool, fur, leather, feathers, etc. They develop slowly and may feed for up to 10 mo.
Identification
Cloths Moth are about .25 inch long and have silvery wings. They usually remain in the infested material and do not fly to lights. The caterpillars are white with a brown head.
Treatment
Thoroughly inspect all potential sites and material inside. Dry clean clothing and store in sealed containers. Vacuum infested sites to remove caterpillars and adults. Spray insecticide in cracks and crevices.
Cat Flea — Ctenocephalides felis

This flea remains on the host and periodically sucks blood. The eggs are laid in the fur but they fall to the ground or floor. The larval stages are in carpeting or other material and feed on organic matter.
Identification
The cat flea is about 1/16 in. long, dark brown, and flattened from side to side. It has strong hind legs and can jump from the host to another surfaces.
Treatment
Animals should be treated to reduce the adult fleas.Inside vacuum to remove eggs and larval food from carpet. Shampooing will kill larvae. Insecticide treatment will also provide control.
Clover Mites — Bryobia praetiosa

Clover mites live in grass and feed on plant fluids. They do not bite people or animals. In the spring their populations increase rapidly and mites leave the turfgrass and climb on houses, and enter through windows, doors, and cracks.
Identification
These red,brown to black mites are about 1/16 of an in. long.
Treatment
Use a vacuum cleaner to remove them inside. Wash them from the outside of the house with a hose.
Drugstore Beetle — Stegobium paniceum
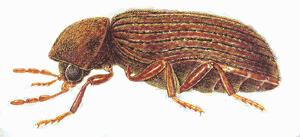
The larvae attack a variety of foods like cereals, flour and meal. The larvae can penetrate food packaging. The life cycle lasts about 3 to 7 mo.
Identification
The adult is about 1/8 in. long and is brown with short yellow hairs on the wings. The young stages are yellowish br. with a dark head.
Treatment
Discard all infested material and vacuum the infested areas. Pheromone traps may be used to reduce infestations in food areas.
Earwig — Forficula sp.

Earwigs feed on plant material such as flowers, but also feed on other insects. The adults lay their eggs in moist soil in the spring. They enter houses through doorways and windows, but usually do not become established inside.
Identification
These insects are about 1 in. long, reddish brown in color, and have pincers at the end of their abdomen. They are commonly found in large groups under debris, rocks, and flower pots around the outside of houses. Inside they may occur in kitchens and bathrooms.
Treatment
Removing as much of their preferred harborage (under flower pots or other flat objects) around the house will reduce outside populations. Sealing door thresholds and around windows may also be helpful inside.
Elm Leaf Beetles — Xanthogaleruca luteola

The young stages of these beetles feed on the leaves of trees, usually elm trees; they can be very numerous in some areas. The adult beetles are found in protected places outside or in attics and garages.
Identification
These beetles are about .25 in. long and they are green or brown with a black stripe on their sides. They are common in late summer and fall.
Treatment
Vacuum the beetles from carpet or windows. Treat attic spaces when large numbers of beetles are found inside.
Field Cricket — Gryllus spp.

The eggs hatch in spring and develop slowly during the summer. They feed on plant material around houses. Adults appear in the fall and are often found outside of buildings on cool days. They may come inside through doors or windows.
Identification
This cricket is about 1.25 in. long, black with short wings. The female has a pointed tail. It is the most common cricket in the fall.Adults are active and chirping during early evening.
Treatment
Limit mulch and protective vegetation on the sunny side of house to keep crickets away. Spray the soil around the house with a garden insecticide to eliminate them.
Flatheaded Borer — Buprestidae

Adult beetles lay eggs in crevices that develop in logs. Larvae hatching from the eggs bore directly into the sapwood portion of the wood and begin feeding. However, as infested wood begins to dry, larvae will tunnel deeper. Larvae prefer moist wood . They do not feed in the heartwood. Flatheaded wood borers may complete their development from egg to adult within 1 year. However, their life cycle may extend to 5 years.
Identification
Flatheaded borers are often shiny and brightly colored. The larvae are referred to as flatheaded wood borers, because the body area behind the head is enlarged and flattened. Flatheaded borers are important pests in forests.\r\nDamage results from larvae boring into sapwood of recently felled trees. Larvae will feed on a variety of woods. Flatheaded wood borers can be pests of modern loghouses, and infest furniture and fences.
Flour Beetle — Tribolium spp.

The eggs are laid in the flour or grain. The adults may crawl or fly away from the site to infest other products.
Identification
The flour beetle is about 1/8 in. long and brownish red. The antennae are short . They are often found in grain and flour products.
Treatment
Inspect all flour and grain products. Empty cabinets or pantry and vacuum thoroughly.
Fruit Fly — Drosophila spp.

The adults are attracted to the odors of decaying fruits and vegetables. The eggs are laid directly on the food. They can complete their life cycle in 5 to 10 days. Adults live for 30 days.
Identification
Fruit flies are about 1/8 in. long. They are light brown, with clear wings and red eyes. The maggots are small and white.
Treatment
Refrigerate fruits and vegetables, and cover garbage. Inspect for breeding sites inside and outside. Vinegar placed in a shallow pan overnight will trap adults.
Fungus Gnat — Sciara spp.

In the household, fungus gnats are usually found around potted plants because both the adult and the larvae require a humid environment. The larvae can complete their development by feeding on the moist and decaying matter in potting soil. The lifecycle may be completed in about 10 days, and the adults may live about 2 wks.
Identification
These small flies are found around decaying vegetation. They have large wings and long antennae, but they are poor flyers and do not move far from their breeding site.
Treatment
Control by letting soil completely dry between watering. This will kill the larvae.
German Cockroach — Blattella germanica

This cockroach remains inside and infests kitchens and bathrooms. A large populations my develop when there is plenty of food and water. The female produces about 40 eggs per mo. for about 6 mo.
Identification
The adults are about .5 in. long and light brown. There are 2 black stripes on the body behind the head. The young stages lack wings and have 2 dark brown stripes. The egg case is about .25 in. long and brown.
Treatment
Removing food and water will help to limit these pests. Use sticky traps to locate infested sites. Chemical control in the form of sprays, dusts or baits may be necessary to control heavy infestations.
House Centipede — Scutigera coleopterata

The house centipede lives inside and out. They occurs in damp locations such as basements and bathrooms where it preys on insects. There are several larval stages before reaching maturity. The adults and young may be found together.
Identification
This centipede is about 1 in. long and the body is yellowish gray with dark stripes. There legs are very long. The antennae are also long and go out in front of the body.
Treatment
Reducing the presence of insects and may help to limit populations. Aerosol sprays , dusts in cracks and crevices, and sticky traps may also be used.
Indian Meal Moth — Plodia interpunctella

The adult moths usually stay close to the breeding site, which is flour or meal but can also include pet food, seeds, chocolate and other household foods. The caterpillars create webs over the surface of the food they are infesting.
Identification
This moth is distinguished by the wings being gray at the base and reddish brown at the outer portion . The moths usually fly in the evening. The caterpillars are about .5 in. long and colored yellow to light green. They may be found among webs in the infested food.
Treatment
Removing and discarding all infested food to eliminating this pest. Vacuuming spilled flour and other foods will be effective in control. Keep foods in sealed containers.
Lone Star Tick — Amblyomma americanium

The young and adult stages of this tick are parasites of small and large animals. The 3 immature stages require a blood meal from a different host in order to develop to the adult stage and to lay eggs.
Identification
This tick is about 1/8 in. long and is dark brown. It has a white spot in the center of the back, or may have several white spots on the rear of the back.
Treatment
Keep vegetation cut low to discourage small animal populations. Use repellents on clothing when walking in areas infested with ticks. Liquid spray and granular insecticides applied in the spring provide some control.
Longhorned Beetle — Cerambycidae

There are several kinds of "sawyers" including, southern pine sawyer, white-spotted sawyer and balsam fir sawyer. The adults appear in the spring and chew holes in the bark of recently felled trees and insert eggs. The young larvae bore beneath the bark for about 2 mo.; later they enter the wood to make a deep cell through the sapwood and heartwood. The larvae pupate in the spring and the adult emerges in about 30 days to mate and lay eggs.
Identification
Longhorned beetles can be found infesting unseasoned soft or hardwood. These beetles live only in unseasoned wood and have short life cycles. The damage caused by these species is limited.
Treatment
Spraying trees with a pesticide mixed with an oil based liquid,\r\nsuch as dish soap is sometimes effective in keeping these pests from laying eggs on the trees.
Millipede — Loxoceles reclusa

They live in dark, moist habitats and feed primarily on decaying vegetation. They may occur in the thatch in the lawn, in the mulch around the house, and in piles of leaves and grass clippings. When conditions are good large populations may develop in one location. Large numbers of millipedes may move from their breeding site to other locations, patios and into houses through ground-level doors.
Identification
Identified by their semicircular shape and numerous legs, they have 2 legs per body segment. Their size varies from a .5 to 2 in.. Their color varies from brown to yellowish. They roll into a ball when bothered.
Treatment
Removing decaying vegetation and excess mulch will eliminate potential breeding sites . Chemical control is not as effective because they are not easily killed with chemicals.
Mosquitoes — Culex spp., Anopheles spp., Aedes spp.

The young stages of mosquitoes live in standing water and feed on microscopic organisms. The adult females are parasites and require a blood meal to develop their eggs.
Identification
They are small flies that are active in the evening. They are characterized by white markings on their legs and wings.
Treatment
Remove open containers that can hold water, especially old tires, flower pots, and buckets,ect. ect. Prevention is the best control for these flies.Sprays may help also.
Moth Fly — Psychoda spp.

The young stages of moth flies live in the organic debris in drains, and in sinks and toilets. The lifecycle requires about 30 days to complete and the adult flies may live about 3 wks.
Identification
This small gray colored fly is characterized by having "hairy" wings so that it looks like a moth. They are commonly seen flying in bathrooms.
Treatment
Thoroughly cleaning around sinks and toilets may help to eliminat them. When large numbers of these flies are present there may be a clogged drain. Temporary control can be achieved by pouring boiling water down the drain, then removing all the debris.
Old House Borer

The adult beetle is 5/8 to 1 in. long, slightly flattened and black to brownish-black. The area behind the head is rounded with two shiny areas on each side. The wing covers may be completely black or with patches of gray that form bands. The larva is cream colored; the mandibles are dark brown. Full grown larvae may be 1.25 in. long. There are 3 distinct, dark colored eye spots on each side of the head. The old house borer spends 2 to 10 yrs. of its life in the larval stage.
Identification
The old house borer is a pest of structural and ornamental wood around the world. The larval stage feeds on seasoned softwood timber. Larvae will not live in rotten wood, and the oils and resins of the heartwood portion of the wood make it undesirable. They infest wood that is less than 10 yrs. of age. Larvae can feed for several years in seasoned softwood, and cause structural damage to infested material.
Treatment
Treat wood at the first sign of infestation. Can sometimes be spotted by the sawdust they leave when boring, also can be heard boring in wood sometimes.
Orb Weaver Spider

They are usually common in late summer and fall. They build their large webs in areas that have a lot of insects. This usually brings them to locations near lights on porches, patios and around doorways.
Identification
These spiders are often large, about .5 in. long, and brightly colored yellow and black, or red and yellow. They build large, circular webs around doorways and on vegetation.
Treatment
Remove the webs in the evening. Reduce the use of lights near doorways. These spiders are not dangerous, and are beneficial because they eat other insects.
Oriental Cockroach — Blatta orientalis

This cockroach mainly occurs outdoors, but will also infest basements and other cool and damp locations. It can live in cold temperatures and is often active in early spring.The female produces an egg case every mo. for about 8 mo.; there are about 14 eggs per egg case. The adults do not fly.
Identification
The adults are about 1.25 in. long and blackish-brown. The wings are short in the female and absent in the male. The young are blackish-brown and have no wings. The egg case is about 3/8 in. long and black.
Treatment
Limiting the available sites, and reducing the food available will help control them. Sticky traps may help to control the individuals that forage indoors. Chemicals in the form of sprays, dusts or baits will help in controlling these pest.
Pavement Ant — Tetramorium caespitum

These ants are common in the yard, garden and around foundations. They feed on plant and animal material. They forage during the day.
Identification
These ants are about .25 in. long, and the body is brown with light brown legs. The winged forms may occur during warm months, but are most common in June and July. Nests are located in soil and in the masonry walls of buildings.
Treatment
The best control is to locate and treat the outside nests with liquid insecticide, and to use bait for the inside nests. Colonies that are foraging inside will usually be located close to the foundation.
Pharaoh Ant — Monomorium pharaonis

Establishments may consist of a few hundred to thousands of workers and queens. They are often located in more than one sites in the infested structure. They will feed on a variety of foods, but prefer meat and grease, and forage during the day and night.
Identification
These light brown ants are about 1/8 in. long. They establish nests inside, and are common throughout the year.
Treatment
Spraying for these ants should not be done because it mite fragment the colonies and worsens the problem. Baits placed in all locations that the ants have been seen is the best, but baiting may take several months to work.
Phorids — Phoridae

These flies may breed in clogged drains,and in septic drains and sewer pipes that are leaking into the ground.
Identification
These small flies are about 1/8 in. long. They are similar to other gnats except that they have an erratic walk.
Treatment
Check all areas that have organic matter, such as sewer lines and other drain pipes, both inside and outside.
Psocids — Liposcellis sp.

They develop from egg to adult in about 65 days, and feed on microscopic fungi and molds in damp areas.
Identification
Yellow insects that are about 1 millimeter long , and short legs and antennae. They usually remain in damp secluded areas.
Treatment
Remove and discard infested material, vacuum well. Reduce hiding areas such as old books and magazines. Lower the relative humidity for several days.
Pseudoscorpions

Pseudoscorpions are predators on mites and spiders. They live in wooded areas outside.
Identification
These small animals are reddish brown and have a large pair of front legs and they resemble a scorpion with a short tail.
Treatment
Remove from clothing and vacuum carpeting. They do not bite or sting.
Silverfish — Lepisma saccharina

Silverfish prefer cool and damp areas. They are usually found in kitchens and bathrooms, and basements. They feed on microscopic mold and fungi that grows in these locations. Adults and young have similar habits; and adults may live for more than 1 year.
Identification
These silvery gray insects have 3 long tails at the end of their body. They have long, antennae, the body is about .5 in. long. They are active at night and remain in protected areas during the day.
Treatment
Removing piles of paper, magazines and books from damp areas help limit infestations. Cracks and crevices in areas where they have been seen should be treated with spray insecticide; cockroach baits may be effective in controlling infestations.
Sowbugs and Pillbugs

They live in damp areas and feed on decaying organic matter.
Identification
These animals are about .5 in. long and are gray to brown in color. They move slowly and curl up when bothered.
Treatment
Remove excessive mulch and decay from around doors. Make sure doors and windows seal tight. Use a vacuum to remove from carpets.
Springtails — Collembola

Springtails live in damp areas where they feed on decaying organic matter. They are common in soil, but they can move inside.
Identification
These insects are about 1/8 in. long and their color range form gray to black. They hop when bothered.
Treatment
Remove excess mulch and decay from around doors and windows. Check seals on doors and windows, make sure of a tight fit. Use a vacuum to remove from carpeting.
Thief Ant — Solenopsis molesta

Colonies located outside under rocks or around walkways, in rotting wood or soil. Colonies may be a few hundred to several thousand workers and queens. They also nest inside where they feed on meat and grease and are known to bite.
Identification
These light brown ants are about 1/8 in. long. The winged forms are produced in late summer. Nests may be located in soil next to other ants or around foundations or inside.
Treatment
Locate and treat the outside nests with liquid insecticide and to use bait for the inside nests. Colonies that are inside will usually be located close to the foundation.
Velvet Ant — Mutilidae
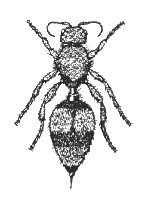
They are actually wasps, but appear to be ants. They are parasites in the nests of ground-nesting wasps such as yellowjackets and solitary bees. They can be somewhat aggressive and will sting if bothered.
Identification
This ant is about .75 in. long and are usually black and red, and they have a fuzzy body.
Treatment
Velvet ants do not infest houses and are not a threat to people or pets, and can be controlled with an spray.
White Fly — Trialeurodes vaporariorum

Whiteflies are small insects that typically feed on the undersides of plant leaves.
Identification
Flies have yellowish, soft bodies and white wings and will scatter when disturbed. When feeding will leave behind "honeydew" which can attract ants and grow fungus. Eggs develop into waxy looking nymphs and larva.
Treatment
Spray the underside of leaves with an insecticidal soap.
Woods Cockroach — Parcoblatta pennsylvanica

Wood roaches live in rotted logs, tree stumps, hollow trees, wood piles, and under the loose bark of standing trees and firewood. The males fly to lights at night. The females remain at the nesting site.
Identification
The adults are about 1 in. long, light brown and yellow margins on the area behind the head and the tip of the wings. The female has short wings and can not fly.
Treatment
Remove sites like woodpiles, rotting logs and dead trees may help with control.
Yellow Ant — Acanthomyops spp.
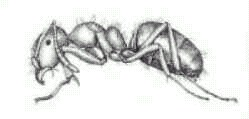
Yellow ants remain in their nests most of the time. They feed on the honeydew from aphids and other insects on the roots of plants. Nest produce swarms during the spring and these may be confused with termite swarms.
Identification
Yellow ants are light to dark brown,and about .25 in. long. The winged females are somewhat bigger, and the wings are clear to pale yellow. Nests may be located in soil next to foundations or sidewalks.
Treatment
Find the nest,they are usually next to foundations or in the soil in the mulch around buildings. Nests can be treated with a insecticide.
Yellowjacket — Dolichovespula spp. , Vespula spp.

The nests are made in the spring and remain active for only 1 year. The workers look for caterpillars and other insects to feed the young, and will defend the nest by stinging . The colony will not survive the winter.
Identification
Yellowjackets are stinging insects about .5 in. long and are colored yellow and black or white and black. They are social insects and live together in nests in the ground or in trees, shrubs or structures.
Treatment
Nest should not be bothered unless a threat to people or pets. Special aerosols can penetrates the nest to kill the colony. Liquid pesticides can be applied to ground nests.